A loopback is commonplace amongst the equipment used when testing data center networks but what is it and how does it work?
A loopback or loop-back is the routing of a signal, back to its own source without modification or repetition of the signal.
In telecommunications, it is often used to test the stability or quality of a signal path to ensure it is free from errors, known as bit errors. This process can be carried out directly at the equipment interface or extended to allow assessment of the installed cable plant, feeding the sent signal back to the receive port of the equipment.
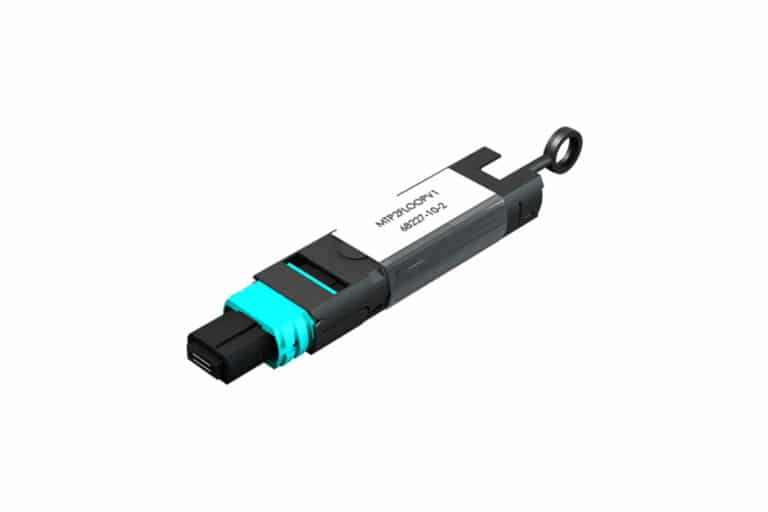
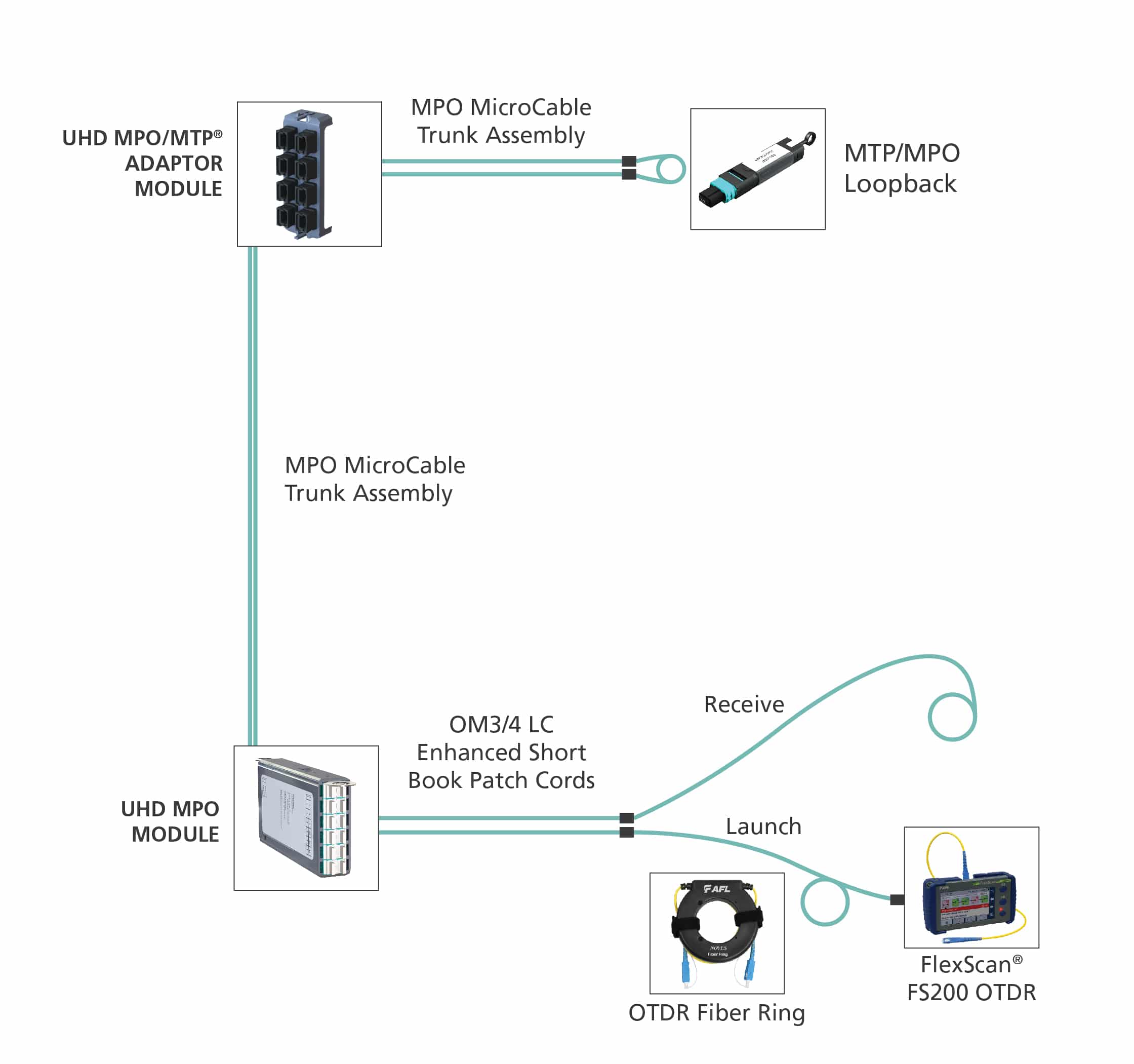
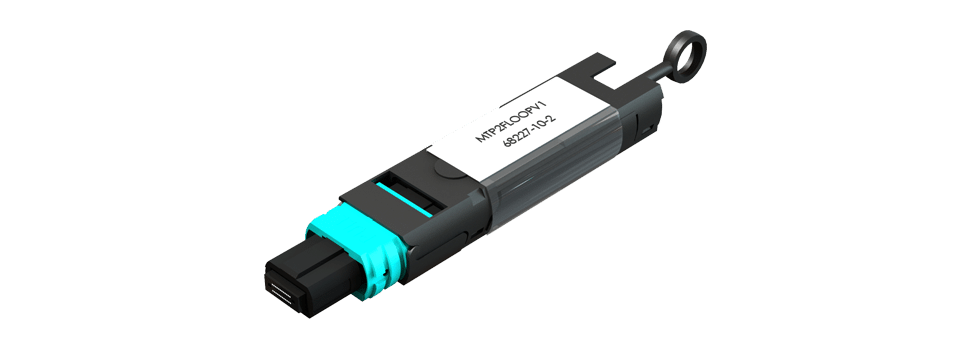
When assessing duplex fiber channels, this can be carried out with the use of a loopback or a short simplex patch cord connecting the separate transmit and receive ports together at the far end. However, when attempting to carry out the same procedure on a device using an MPO/MTP® port such as those found on 40G QFSP+ or 100G CXP/CFP interface, it becomes more challenging due to the interface housing both the transmit and receive ports within the same connector.
In such instances where an MPO/MTP loopback is required, the exact type needed is dependent on the interface under test. Loopbacks are available in a variety of configurations to accommodate 8 fiber, 12 fiber and 24 fiber MPO/MTP connectors and several fiber configurations to suit the interface under test.
Below is a practical example of an MPO/MTP loopback used in a data center environment: